Significance
Climate change is a key factor having an impact on sustainable development and human well-being. Subsequently, it becomes the global issue drawing participation across the globe to lower GHG emissions and alleviate its impacts. Many countries have jointly set up common goals to decrease GHG emissions in order to control a rise of the earth’s average temperature to well below 2 degrees Celsius. As a result, the policies and applicable laws have been established in many countries to foster GHG emission reductions and efficient energy consumption, such as a system permitting to trade GHGs or the “Emission Trading Scheme” (ETS), limitation of fuel consumption for energy production, promotion of more renewable energy investments, and carbon tax, etc. Hence, these are both challenges and significant opportunities for BPP to grow in the energy business.
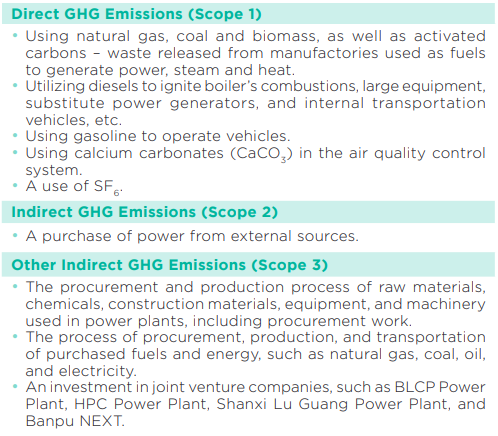
BPP’s GHG emissions activities are summarized as follows:
Management Approach
As BPP operates a power and energy generation business, it directly consumes fuels for energy productions. Consequently, BPP mainly focuses on reducing direct GHG emissions (Scope 1), mainly from fuel consumption. BPP’s direct GHG emissions are equivalent to 99% of its total GHG emissions amount since its operations are the upstream business, generating power and other energy supplied for industrial and residential consumptions.
BPP sees the opportunity and capability to lower GHG emissions by improving energy use efficiency, minimizing losses in the production process, and conducting a study on alternative fuels to achieve its GHG reduction target. It is also looking for opportunities to invest in the energy infrastructure and the battery energy storage system (BESS).
BPP closely monitors on policy changes and assesses risks associated with climate change in preparation for adapting itself to a transition of policies, and applicable laws in various countries. For example, implementing a business continuity management system, reviewing risks and opportunities relevant to climate change in accordance with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), including determining the carbon pricing for consideration on investing in various projects.
Structures of Climate Change Governance

BPP uses management approaches to reduce GHG emissions in various businesses as follows:
- Existing Thermal Power Plants
- The combined heat and power (CHP) plants, in which BPP has management control, consisting of the three CHP plants in China, have high energy efficiency. As a result, the CHP plants’ energy
loss during their maximum production capacity of power and steam is 25%, while the thermal power plants solely generating electricity will lose energy around 65% once producing power. As a result, the CHP plants have low energy consumption rate and marginal GHG emissions intensity. Customer’s demand for steam in certain periods, however, directly affects the energy efficiency and GHG emissions of CHP plants. BPP, therefore, focuses on utilizing innovations to improve its power plant’s efficiency and production processes, as well as to operate the power plants to be flexible in response to dynamic demand for steam. In addition, the experiment has been conducted by
burning biomass together with coal to reduce the amount of carbon emissions. Besides, BPP together with Banpu Group has verified the accuracy of GHG emissions database. Thereby, all three CHP plants have been inspected and certified for GHG emissions since 2018 to present. Moreover, the CHP plants are also looking for business opportunities to become an integrated energy producer and provider, such as installing solar cells on rooftops for government agencies, etc. - The gas-fired power plant, in which BPP has direct control,
namely Temple gas-fired power plant, located in the United States of America has high energy efficiency and uses natural gas in generating power supplied to the merchant power markets. Since the gas-fired plants emit lower GHG emissions than the thermal power plants, BPP focuses on managing and carrying out the annual maintenance continuously to meet the quality standards. This will affect the power plant’s efficiency in terms of GHG emissions intensity and energy consumption rate, water use rate and a reduction of losses in the production system. In addition, a joint verification on accuracy of GHG emissions database has been arranged together with Banpu
Group. Temple gas-fired power plant has been examined and certified for GHG emissions data since 2023 to present. - The joint-venture thermal power plants, namely BLCP Power
Plant, HPC Power Plant, and Shanxi Lu Guang Power Plant focus on quality management and efficient annual maintenance, including using the information system to predict a machinery maintenance before it is broken down (Predictive Maintenance), etc. This will affect the power plants’ efficiency on reducing the fuel consumption per unit of products and maintaining the availability factor (AF) as designed. It is also a key performance indicator reflecting the power plant’s availability and efficiency and directly resulting in decreasing the GHG emissions intensity. The Asset Management Unit is assigned to jointly monitor the power plants’ GHG emission operations with the business partners who have invested in such power plants. In addition, activities to reduce GHG emissions are promoted, such as a use of electric trucks to transport limestone at HPC Power Plant,
a project to conduct a feasibility study on using ammonia as a substituted fuel at BLCP Power Plant, a project to conduct a feasibility study on installing solar cells, constructing a small hydroelectric power plant, and using biomass at HPC Power Plant, etc.
- The combined heat and power (CHP) plants, in which BPP has management control, consisting of the three CHP plants in China, have high energy efficiency. As a result, the CHP plants’ energy
- Renewable Power Plant and Energy Technology Projects, which
are the joint-venture companies. BPP has invested 50% of stakes in Banpu NEXT to operate the renewable energy generated from solar power plants and wind power plants, including the energy technology business as
well as the clean energy generation service together with the integrated energy management solution to reduce GHG emissions, such as the solar power generation system on the rooftops, the energy storage system, the electric vehicle business, the smart community development business and the energy management system business, etc. In addition, BPP is also expanding its clean energy business in the United States of America by investing in the construction of a 2.5 MW Ponder Solar Power Plant, located
in the Barnett Shale of Banpu Group. The aim is to respond to the clean energy demand in the power merchant market. - Renewable Power Plant and Energy Technology Projects, BPP has a policy of not investing further in coal-fired power plants. It determines investment strategies towards the highly-efficient and environmentally-friendly power plant projects by focusing on gas-fired power plants, which consume stable fuels for production. Additionally, the gas-fired power plant has high flexibility in adjusting its production in response to demand in the power merchant market. BPP also continues investing in renewable energy and energy technology through Banpu NEXT as well as looking for investment opportunities in a small nuclear power plant, which is considered as one of the clean energy patterns, having a tendency to grow in the future.
- Carbon Reduction Projects, BPP sets up strategies for conducting business sustainably and responding to GHG emissions reduction. Therefore, a target on EBITDA proportion from a low-carbon business has been set out to be at least 65% by the year 2030. In addition, BPP began investing in the Cotton Cove project in the U.S., which employs the Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technology. The Cotton Cove project is a joint-investment between BPP and BKV dCarbon Ventures Company. Moreover, BPP is also looking for opportunities in the environmentally-friendly energy business, such as ammonia, hydrogen, fuels from biomass, etc.
Data Collection:
The amount of diesel, biodiesel, and benzene is compiled by accumulating figures from receipts, while the coal quantity is obtained from a scale attached to a conveyor belt before being proceeded to the power plant’s production process.
Meanwhile, the amount of flue gas is collected from gas flow meters. As for natural gas used in the production of power plants in the United States of America, it is obtained from meters measuring the heat value according to actual use.
A calculation of energy consumption volume:
BPP uses the energy conversion factor based on the GHG Protocol: Emission Factors from Cross Sector Tools for calculating the consumption volume of diesel, biodiesel, and benzene. Meanwhile, the consumption of coal and waste
gas is gathered from expenses incurred from the monthly
measurements.
Calculation of GHG emissions amount:
BPP collects the amount of GHG emissions only for businesses, in which it has
operational control by using the “Global Warming Potential” (GWP), with reference to the “Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report” (AR5). The emission factors used are based upon “A Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard (Revised Edition)”, while specific coefficients will be used if there is a region-specific emission coefficient. The gas used in GHG emissions’ calculations consists of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6).
Performance
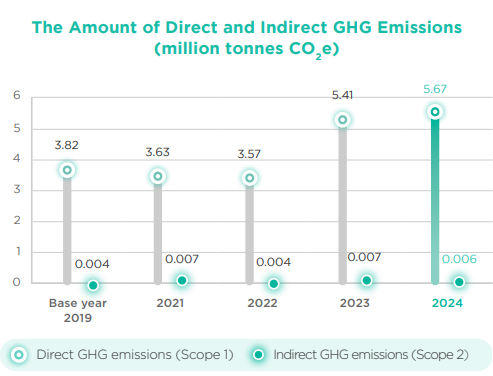
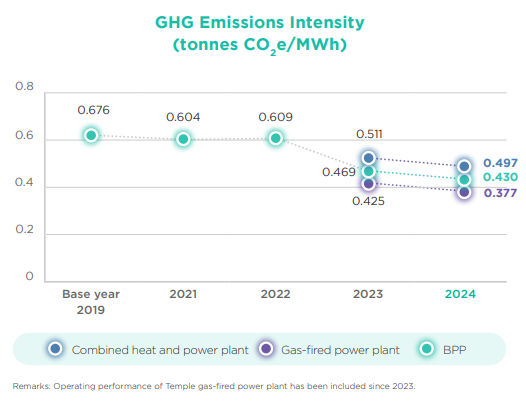
- The GHG emissions intensity (Scope 1&2) was 0.430 tonnes CO2e/MWh, decreasing 21.7%, when compared with the target set
- The GHG emissions intensity of CHP plants was 0.497 tonnes CO2e/MWh.
- The gas-fired power plant’s GHG emissions intensity was 0.377 tonnes
CO2e/MWh.
- EBITDA proportion from low-carbon energy business was equivalent to 27%.
- The renewable energy generation capacity was 410 MW.
Other Indirect GHG Emissions (Scope 3)
Since 2023, BPP has assessed other indirect GHG emissions (Scope 3) throughout the supply chain by using the criteria in accordance with the World Resource Institute (WRI) Greenhouse Gas Accounting Standards to determine the relevance of activities in 15 categories. In 2024, other indirect GHG emissions (Scope 3) totaled 14,066,691 tonnes CO2e from the following activities:
| Activities | Association with BPP | The Amount of GHG Emissions (Tonnes CO2e) | Calculation Methodology |
| Category 1 Purchased goods and services | Being involved with the procurement and production process of raw materials and chemicals used in the power plants and service from contractors. | No calculation is performed due to the minimal proportion compared to other activities. |
– |
| Category 2 Capital goods | Being involved with the procurement and production process of capital good purchased such as machinery, spare parts, vehicles and construction materials used in the power plants and offices. | 255,693 |
|
| Category 3 Fuel- and energy related activities | Being involved with the production procurement process and transportation of purchased fuels and energy, such as natural gas, coal, oil, and electricity |
1,092,748 |
|
| Category 4 Upstream transportation and distribution | Being related to the transportation of power plant’s raw materials and machinery carried out by partners or contractors. | There is no calculation since natural gas is delivered via pipelines, while other fuels, such as coal and oil are from various trading partners. This activity is, therefore, only a small portion when compared with other activities. |
– |
| Category 5 Waste generated in operations | Being associated with production’s waste management. | No calculation is performed due to the minimal proportion compared to other activities |
– |
| Category 6 Business travel | Being involved with employee’s business trips via airplanes, trains, and cars. | No calculation is performed due to the minimal proportion compared to other activities |
– |
| Category 7 Employee commuting | Being related to BPP employees commuting from their residences to the offices by their own cars, or other public transportation. |
No calculation is performed due to the minimal proportion compared to other activities |
– |
| Category 8 Upstream leased assets | BPP does not lease any assets for production, but it only rents the office spaces. | No calculation is performed due to the minimal proportion compared to other activities |
– |
| Category 9 Downstream transportation and distribution | Not relevant since BPP doesn’t own the power transmission lines, steam, hot and cold water pipelines. |
– | – |
| Category 10 Processing of sold products | Not relevant since BPP’s products are in the energy form, such as electricity, steam and hot water. As a result, these products are not processed. |
– | – |
| Category 11 Use of sold products | Since BPP’s products are in the form of energy, such as electricity, steam, and hot water, the customers’ energy use is an indirect GHG emission (Scope 2). |
– | – |
| Category 12 End of life treatment of sold products | Not relevant because BPP’s products are in the form of energy, such as electricity, steam, and hot water. As a result, there is no waste disposal process for the products. |
– | – |
| Category 13 Downstream leased assets | Not relevant because BPP does not operate an asset rental business and does not have any assets available for rent. |
– | – |
| Category 14 Franchises | Not relevant, as BPP does not operate a franchise business. | – | – |
| Category 15 Investments | Being related to an investment in joint-venture companies, consisting of BLCP, HPC, Shanxi Lu Guang power plants, and Banpu NEXT. |
12,718,250 |
|
Key Activities and Projects
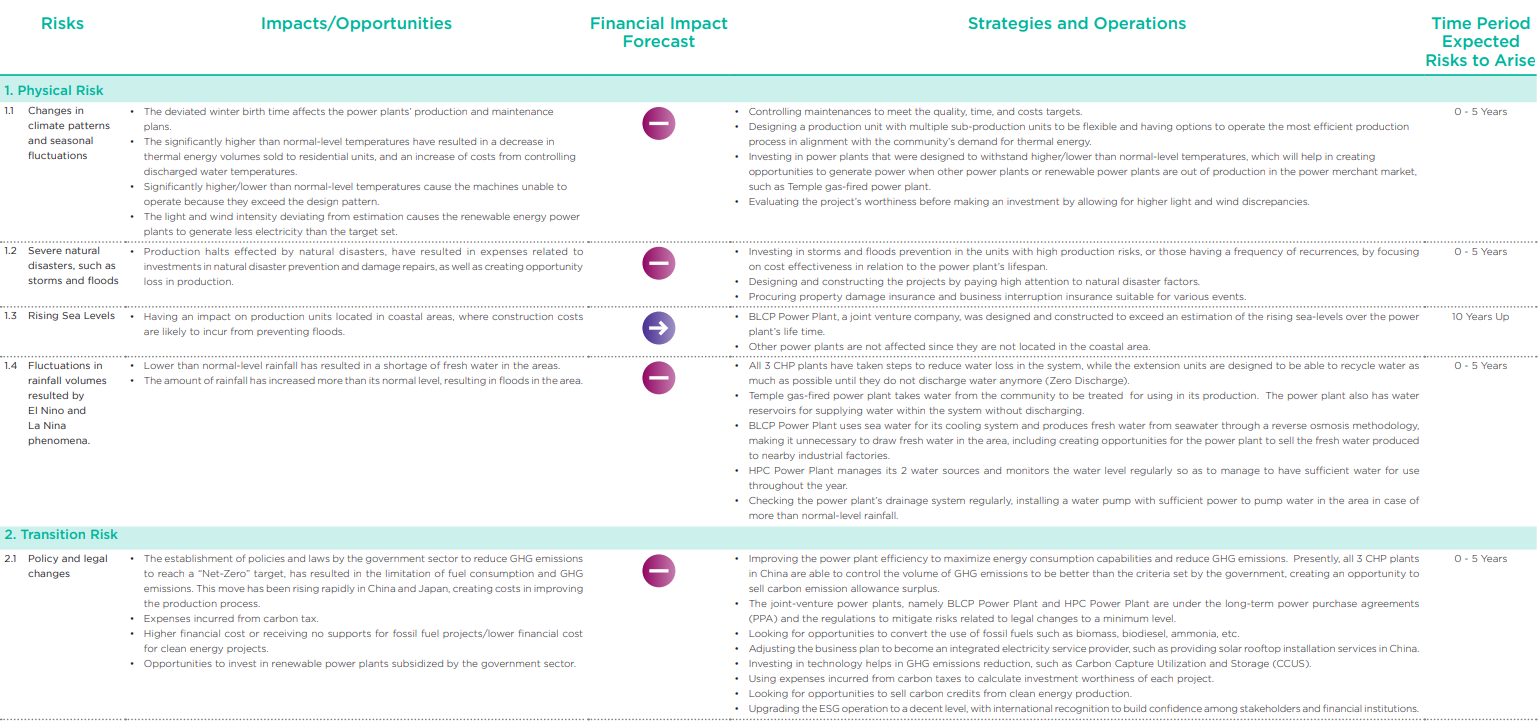
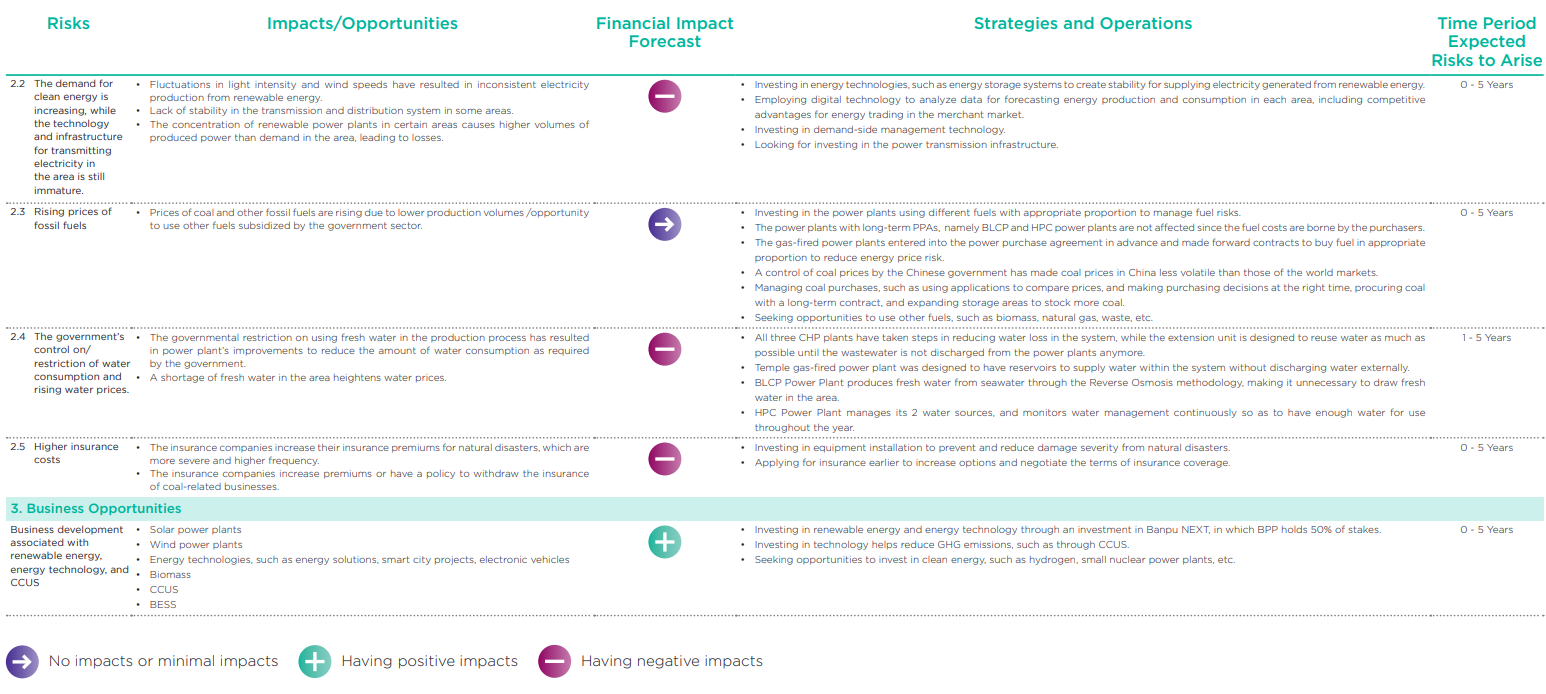
Assessments of risks, impacts, and opportunities resulted from climate change
BPP has assessed risks, impacts, and opportunities arising from climate change during the years 2022 – 2040, with a scope covering investments of all business units with significant investment proportion, or over 30%.
Carbon Pricing
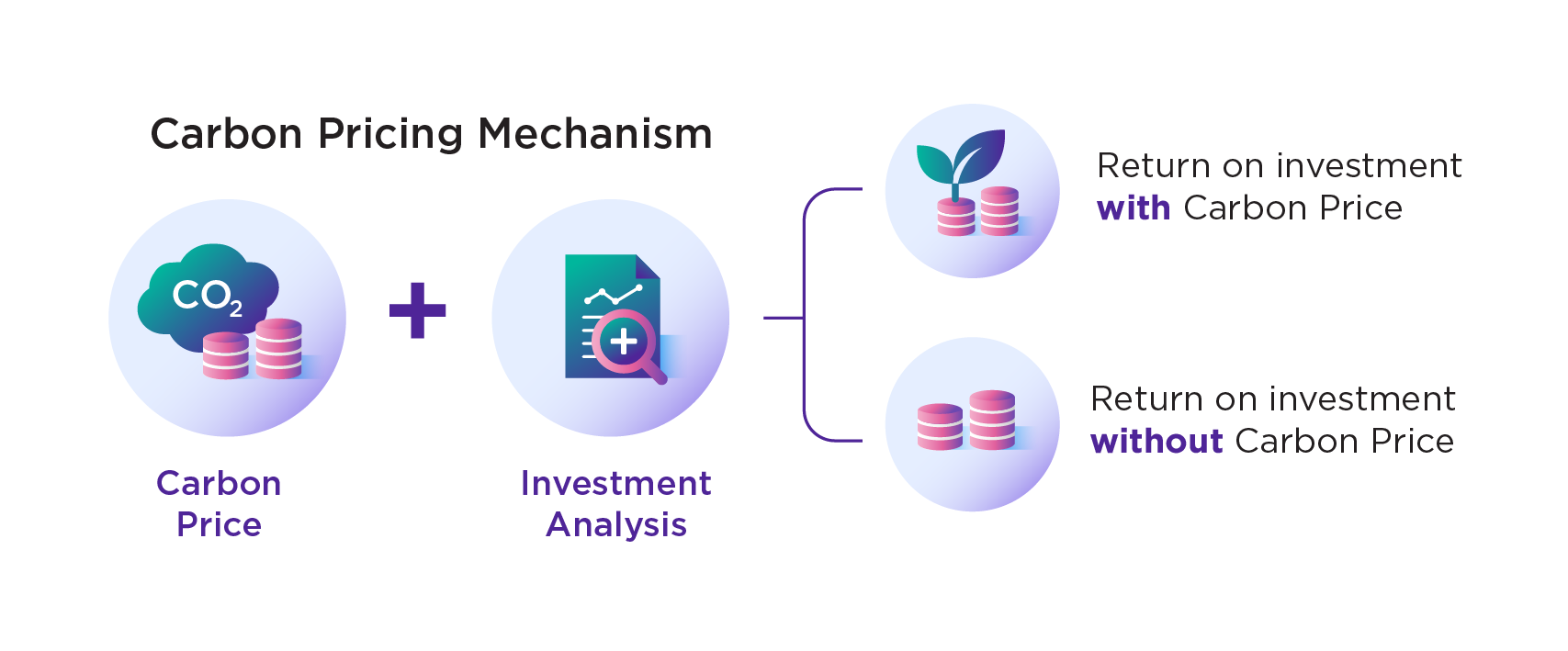
In the past year, the Company used the internal carbon price which would determine the GHG cost in various areas used as part of the cost to analyze the investment value and possibility of new projects in the future. The Company focused on low carbon emission projects and factors to reduce the Company’s GHG emissions reduction in order to achieve the goal set and to be prepared for adaption to the possibility of legal changes and enforcement to reduce GHG emissions in the near future.
The complex to simple boiler slag removal system reform
The original design of the boiler slag removal system of Zouping CHP Power Plant consisted of a slag conveyor belt beneath the boiler, hydraulic slag pumps, water separation tanks in a total of 28 sets, including a slag transport pipeline system with over 1,000 meters long. The analysis on the problem of boiler slag removal system found that 65% of the problems was from slag transportation. This was due to severe corrosion from the high velocity mixture of slag and water. As a result, Zouping CHP Plant has studied and improved its slag transportation system by using a slag conveyor belt together with a slag storage tank to replace the previous system equipped with a water separation tank, a slag transport pipe and a slag pump. This has made the system more efficient. A reduction of device numbers and a decrease of transportation distances can reduce maintenance costs and electricity costs by approximately USD 0.2 million per annum as well as lower GHG emissions by 987 tonnes CO2e/year
Biomass Co-firing to reduce GHG emissions
To meet the requirements of China’s transition towards a green and low-carbon energy production system, Zhengding CHP Plant is BPP’s first power plant to make a trial of co-firing biomass and coal at Boiler No. 2. The aim is to reduce the GHG emissions intensity and increase revenue from selling rights to release the GHG. According to the experiment, it was found that co-firing biomass together with coal can be done stably and efficiently.
Subsequently, Zhengding CHP Plant plans to increase the biomass mixing ratio, starting from the year 2025 onwards. The power plant also sets up a goal to have a biomass mixing ratio of 10% and earning income from selling rights to release GHG of approximately RMB 6.5 million per year by 2026.
Co-firing biomass with coal not only increases the power plants’ revenue and reduces GHG emissions but also decreases the impact of agricultural waste disposal on the environment, including utilizing resources efficiently and helping heighten farmers’ income in the area. In addition, it can stimulate the development of related industrial value chains, create employment opportunities and promote local economic development.

Battery energy storage system project in Japan
Today, the global energy transition is becoming increasingly important. This is because the demand for energy continues to increase in parallel with the need to reduce GHG emissions. Therefore, the battery energy storage system (BESS) is a technology playing a key role in supporting the transition to a sustainable energy system.
BPP uses BESS in the TONO Matsuzaki Battery Park project, selected by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) to be part of the project to support the installation of energy storage batteries in fiscal year 2021, to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy. The TONO Matsuzaki Battery Park project is located on an area of approximately 3,000 square meters in Tono City, Iwate Prefecture.
This project will receive electricity from the system during periods of off-peak demand to be stored in batteries with a total capacity of approximately 14,500 KWs and distribute the power during periods of peak demand. It entered into a long-term power purchase agreement of 25 years. Currently, the project’s construction has been completed and is in the process of grid connection as well as testing the system. It is expected to begin supplying commercial electricity in June 2025.

The path of Banpu Group towards Net-Zero
The path towards the Net-Zero is an effort to reduce GHG emissions, consisting of 3 main steps, including:
- 1. Calculation of GHG Emissions: Banpu Group has calculated and disclosed direct (Scope 1) and indirect (Scope 2) GHG emissions for business operations under Banpu Group’s control. Meanwhile, other indirect GHG emissions (Scope 3) are currently being processed. It plans to fully calculate and disclose the top 3 sources of emissions by 2026.
- 2. Target Setting: In line with its efforts to limit an increase of temperatures to not over 1.5 degrees Celsius, Banpu Group has set a target of reaching the Net-Zero by the year 2050 and reducing GHG emissions by at least 20% by the year 2030, using the year 2023 as the baseline.
- Operations development to reduce carbon: A key success factor to achieve this goal is the implementation of GHG reduction plans, possibly done by changing operations and adopting new technology. Banpu Group has integrated its GHG emissions reduction plans into the annual strategic business meetings. In addition, the projects related to GHG reduction are monitored and supervised by the Climate Change Committee on a quarterly basis.
As part of Banpu Group, BPP has established the Beyond Quality Megawatts strategy in order to achieve its short- and long-term goals, such as utilizing technology to improve the power plants’ efficiency and using biomass in production to release GHGs. In addition, BPP is looking for investment opportunities in the low-carbon energy and energy technology businesses. It also regularly discloses the GHG emissions information verified by external agencies so as to make stakeholders well aware of the operational results according to the goals set.

Document Download
Climate Change Policy