Significance
Fuels used for generating power, steam, and other forms of energy are the major cost of power plants. Consequently, energy consumption efficiency directly affects costs, and competitive advantages, as well as greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Meanwhile, the applicable regulations controlling the amount of coal consumption in China is still the challenge BPP has to adapt itself to immediately cope with such changes, inclusion of enhancing the energy consumption of existing power plants and developing the future power projects to consume less energy and create competitive advantages in the power merchant market, as well as to be part of alleviating the climate change.
Activities associated with energy consumption in the production process include:
- Using natural gas as a fuel for production of gas-fired power plants.
- Utilizing coals as a fuel to produce power and steam of CHP plants.
- Using diesels to ignite boilers and operate heavy machines.
- Using benzenes and diesels for transportation.
- Buying electricity from external sources.
- A use of power using the equipment and systems within the power plant itself to support power plant’s operational efficiency.
- Making a trial on co-firing coal with biomass, industrial waste, and other substances in the power plants.
Management Approach
BPP focuses on managing all of its power plants to have maximum efficiency by using following management approaches:
- Opting to use environmentally friendly technology with high efficiency on energy use.
- Planning for stable and efficient maintenance by creating the appropriate maintenance plan to increase the availability factor (AF), reduce the planned outage factor and the unplanned outage factor, as well as to decrease energy losses from operation stoppages and commencements.
- Improving steam boiler efficiency to have complete combustion.
- Looking for opportunities to reduce heat and energy loss in the system, including reusing the energy.
- Upgrading all auxiliary machinery systems, such as improving the water quality in steam boilers in order to extend the boiler’s lifespan, decrease the amount of discharged water and make-up water in the system.
- Finding opportunities to use other fuels available in the area, improving power plants to be able to use wider fuels, such as biomass fuel, waste gas from metal smelting plants, natural gas, etc.
- Making a plan for fuel procurement from various sources to create alternative fuel procurement with quality and reasonable prices and to mitigate fuel shortage risks.
- Developing an application for integrated energy management in power plants, starting from purchasing, storage, mixing and fuel combustion in the production process.
Data Collection:
- Gas-fired power plant: The amount of natural gas used in electricity production is collected from heat meters based upon actual usage.
- CHP plants: The amount of coal used in power plants in China is collected from a scale at the coal conveyor belt before being fed into the power plant’s production process. Meanwhile, the amount of gas is obtained from a gas flow meter.
- Other fuel quantities, including diesel, biodiesel, and gasoline, are collected from data on the receipt.
Calculation of energy consumption amount:
BPP uses an energy conversion factor based on the GHG Protocol: Emission Factors from Cross Sector Tools for diesel, biodiesel, and gasoline, including monthly measurements for coal and gas.
Performance
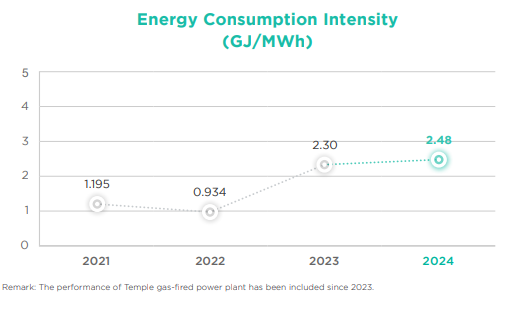
- The energy consumption intensity was 2.48 GJ/MWh.
- Combined heat and power plants’ energy consumption intensity of 0.72 GJ/MWh.
- Gas-fired power plants’ energy consumption intensity of 3.88 GJ/MWh
Key Activities and Projects
Reduction of Power Consumption at Zouping Power Plant
Since the machinery of Zouping Power Plant has long been used while many of its parts were replaced in order to reduce pollutant emissions or a so called “Ultra–Low Emissions”, it has less efficiency and consumed more electricity. As a result, the power plant’s efficiency has decreased as a whole. In addition, Zouping Power Plant has to generate power and steam of which production procedures are different from its initially operational commencement. The Zouping Power Plant, therefore, developed a plan to improve its efficiency and reduce the power consumption ratio of its machinery so as to increase the power plant efficiency.
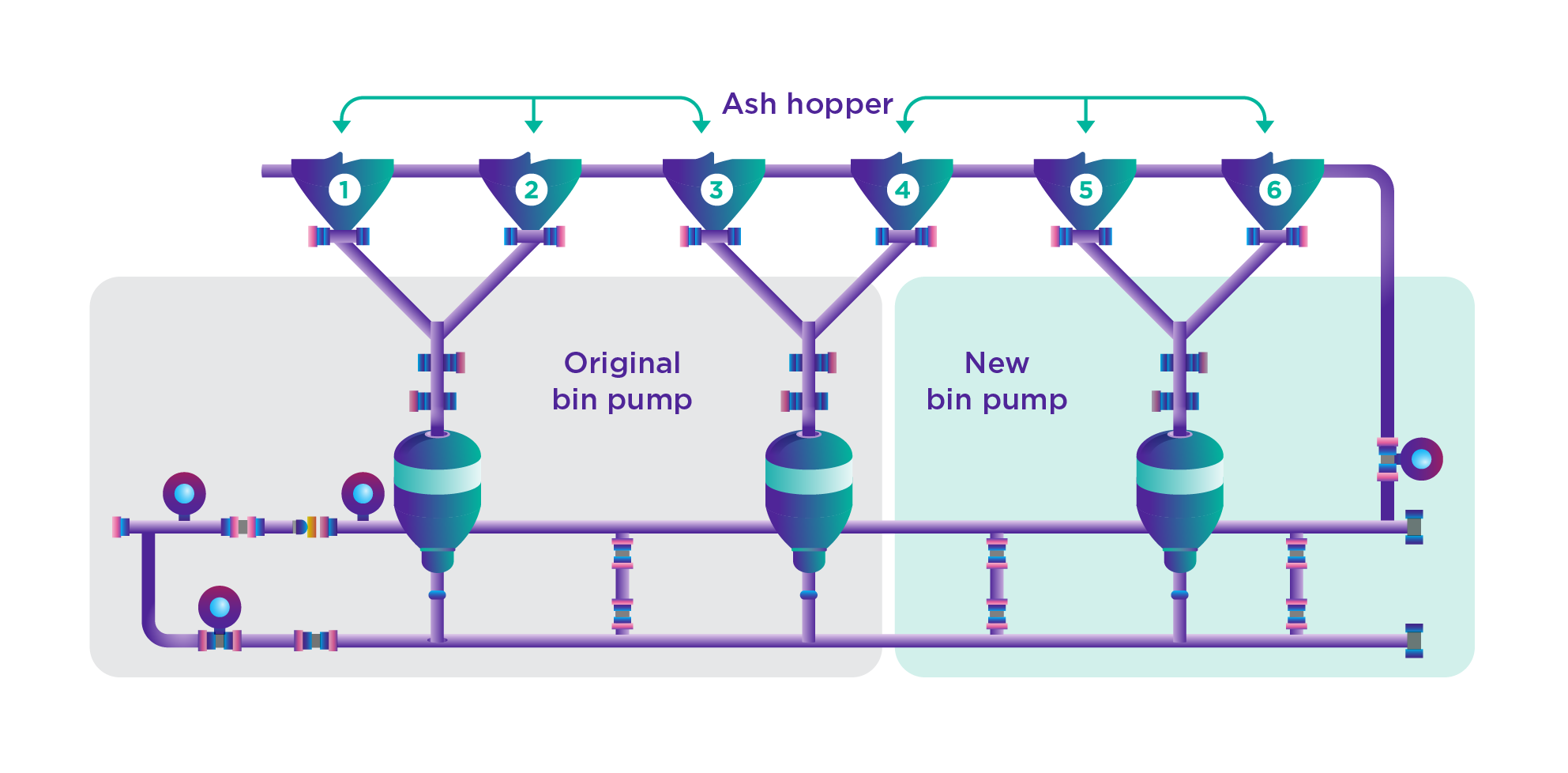
The Zouping Power Plant conducted the engineering study and designing the fly-ash transportation system by installing one more bin pump at the ash hopper No. 5 and No. 6. As a result, there are three bin pumps in the system. Moreover, the existing bin pumps installed at the ash hopper No.1, 2, 3 and at the ash hopper No.4, 5, 6 were moved and installed at the bin pump No. 1, 2 and No.3, 4, respectively, so as to make a balance in the system. As a result, the bin pumps were able to reduce their energy consumption to 1,421,400 KWh per annum, equivalent to CNY 640,000 per annum.
Moreover, Zouping Power Plant also installed the rotational speed control equipment of the forced draft fan at the boiler No.4 and No.6 as well as the induced draft fan at the boiler No.6 in order to reduce the rotational speed. Meanwhile, the power plant has been operated at the low operation mode, which can help reduce energy consumption approximately 50% or 9,290,000 KWh per annum, equivalent to CNY 4,200,000 per annum.
Low Calorific Value Coal Blending at Zhengding CHP Plant
As coal with low calorific value (CV) of about 2,000-3,000 kcal/kg is far cheaper and has more volumes than that with higher heating value of 3,400 kcal/kg, currently used in the market, Zhengding CHP Plant conducted a study and an experiment enabling the plant to use lower CV coal in the steam boilers without compromising on safety, production capacity, and stability as well as reducing the power plant’s fuel costs.
The experiment’s key processes included:
- The process of controlling the calorific value and coal quality after blending coal with different heating values from various sources in a coal stockyard.
- Each boiler’s ooperation process, surveillance, and emergency plans preparations.
- The boiler’s maintenance with an emphasis on additional damage inspection possibly caused by corrosion and special protection.
The experiment’s results showed that the power plant’s equipment has the ability to handle coal with the lowest CV of 2,600 kcal/kg. Zhengding CHP Plant, therefore, is currently using blended coal with an average CV of 2,800 kcal/kg, a reduction of about 600 kcal/kg. This has helped the plant to lower its fuel costs to CNY 37.85 million.